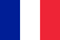
prostatitisis an inflammatory disease of the prostate gland. Manifestations are frequent urination, pain in the penis, scrotum, rectum, sexual disorders (erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation . . . ), sometimes urinary retention, blood in the urine. The diagnosis of prostatitis is established by a urologist or an internist based on the typical clinical picture, results of a rectal examination. In addition, ultrasound of the prostate, bakposv of prostate secretion and urine is performed. Conservative treatment - antibiotic therapy, immunotherapy, prostate massage, lifestyle modification.

General information
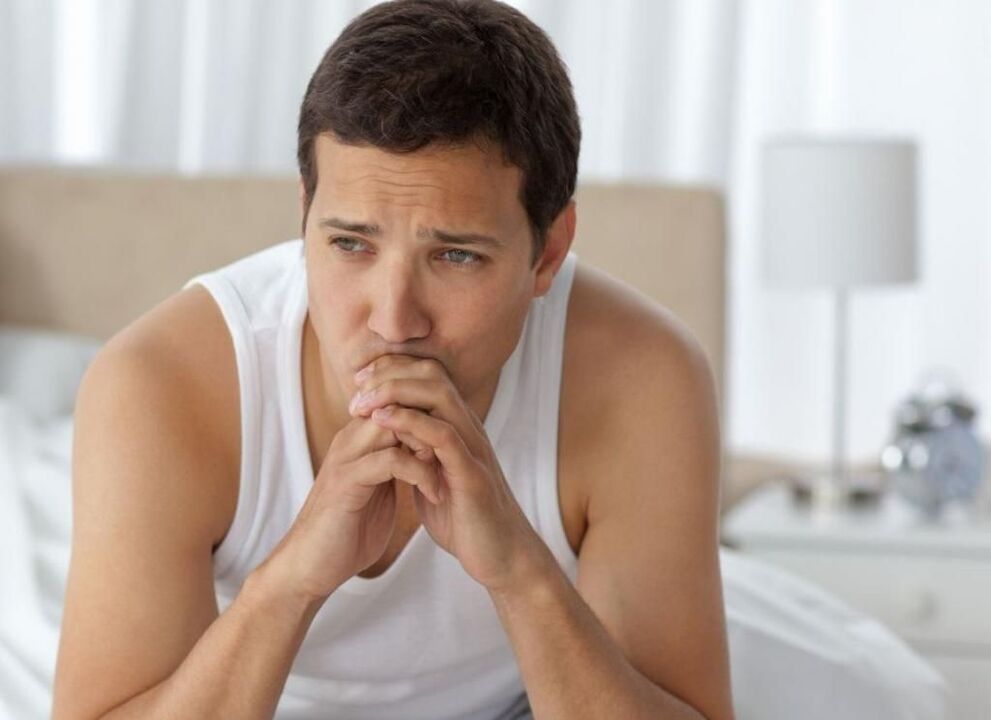
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland (prostate) - the prostate gland. This is the most common disease of the genitourinary system in men. Most commonly affects patients aged 25-50 years. According to various data, 30-85% of men over the age of 30 suffer from prostatitis. Prostate abscesses can form, inflammation of the testicles and appendages, threat of infertility. The proliferation of infections leads to inflammation of the upper genitourinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis).
Pathology develops with the penetration of an infectious agent that enters the prostate tissue from organs of the genitourinary system (urethra, bladder) or from a distant foci of inflammation (with pneumonia, influenza, tonsillitis, boils)
Causes of prostatitis
As an infectious agent during an acute course, Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus), Enterococcus (Enterococcus), Enterobacter (Enterobacter), Pseudomonas (Pseudomonas), Proteus (Proteus), Klebsiella (Klebsiella) and Escherichia coli (E. Coli) can act. Most microorganisms of the flora are conditionally pathogenic and cause prostatitis only in the presence of other predisposing factors. Chronic inflammation is often due to polymicrobial associations.
The risk of developing the disease is increased with hypothermia, a history of specific infections, and conditions accompanied by blockages in the tissues of the prostate gland. There are the following influencing factors:
- General hypothermia (once or permanently, related to working conditions).
- Sedentary lifestyle, a profession that forces a person to be in a sitting position for long periods of time (computer operator, driver, etc. ).
- Persistent constipation.
- Violation of the normal rhythm of sexual activity (excessive sexual activity, prolonged abstinence, incomplete ejaculation during a single "routine" sex without emotional coloring).
- The presence of chronic diseases (cholecystitis, bronchitis) or foci of chronic infection in the body (chronic osteomyelitis, untreated caries, tonsillitis, etc. ).
- Previous urological diseases (urethritis, cystitis, etc. ) and sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea).
- Conditions that suppress the immune system (chronic stress, irregularity and malnutrition, frequent lack of sleep, over-trained athletes).
It is thought that the risk of developing pathology increases with chronic intoxication (alcohol, nicotine, morphine). Several studies in the field of modern andrology demonstrate that chronic perineal trauma (vibration, concussion) in motorcyclists, motorcyclists and cyclists is a predisposing factor. However, the vast majority of experts believe that all these circumstances are not the real cause of the disease, but only contribute to the exacerbation of the underlying inflammatory process in the tissues of the prostate gland.
A decisive role in the occurrence of prostatitis is due to a blockage in the tissues of the prostate gland. Violation of capillary blood flow causes an increase in lipid peroxidation, edema, exudation of prostate tissues and facilitates the development of the infectious process.
Symptoms of Prostatitis
acute prostatitis
There are three stages of acute prostatitis, which are characterized by the presence of several clinical pictures and morphological changes:
- acute enteritis. The patient complains of frequent, painful urination, pain in the sacrum and perineum.
- acute cysts. The pain becomes more intense, sometimes radiating to the anus, worse when defecating. Difficulty urinating, urine comes out in a thin stream. In some cases, there is urinary retention. Hypothermia or moderate hyperthermia are typical.
- acute parenchyma. Severe systemic toxicity, hyperthermia up to 38-40°C, chills. Dyspeptic disorders, often - acute urinary retention. Sharp, stabbing pain in the perineum. Difficulty defecation.
chronic prostatitis
In rare cases, chronic prostatitis becomes the result of an acute process, however, as a rule, a primary chronic episode is observed. The temperature occasionally rises to subfebrile values. Patients noted mild pain in the perineum, discomfort when urinating and defecating. The most characteristic symptom is little discharge from the urethra during defecation. The primary chronic form of the disease develops over a considerable period of time. It precedes prostatitis (stagnation of blood in the capillaries), which gradually turns into bacterial prostatitis.
Chronic prostatitis is often a complication of the inflammatory process caused by the causative agent of a specific infection (chlamydia, trichomonas, ureaplasma, gonococcus). Symptoms of a specific inflammatory process in many cases mask the manifestations of prostate damage. There may be a slight increase in pain when urinating, mild pain in the perineum, urethral discharge rarely when defecating. A small change in the clinical picture usually goes unnoticed by the patient.
Chronic prostatitis can manifest with burning sensation in the urethra and perineum, difficulty urinating, sexual dysfunction, increased general fatigue. The consequences of potency violations (or fear of these violations) often turn into depression, anxiety, and irritability. The clinical picture does not always include all of the symptom groups listed, which vary in different patients and change over time. There are three main syndromes characteristic of chronic prostatitis: pain, dyspepsia, sexual dysfunction.
There are no pain receptors in prostate tissue. The cause of pain in chronic prostatitis is almost inevitable due to the abundant innervation of the pelvic organs, which is involved in the inflammatory process of the nerve pathways. Patients complain of pain of varying intensity - from weakness, pain to severe, sleep disturbances. There is a change in the nature of pain (intensification or weakness) with ejaculation, excessive sexual activity, or sexual abstinence. The pain radiates down to the scrotum, sacrum, perineum, and sometimes to the lower back.
Due to inflammation in chronic prostatitis, the prostate volume increases, compressing the urethra. The lumen of the ureter is reduced. Patients often need to urinate, the bladder feels empty. As a rule, dyspepsia is manifested in the early stages. Then compensatory hypertrophy of the muscular layer of the bladder and ureters develops. Dysuria during this phase weakens, then increases again with decompensation of adaptive mechanisms.
In the early stages, dyslexia may develop, manifesting differently in different patients. Patients may complain of frequent nocturnal erections, faint orgasms, or worsening erections. Rapid ejaculation is associated with a decrease in the threshold of orgasm of the orgasm center. The painful sensation of ejaculation can cause refusal of sexual activity. In the future, sexual dysfunction becomes more pronounced. In the severe stage, impotence develops.
The degree of sexual dysfunction is determined by many factors, including the patient's physical and psychological state. Violation of potency and dysuria can be attributed both to changes in the prostate gland and to the patient's ability to suggest, if he has chronic prostatitis, to expect the inevitable development of the disorder. sexual dysfunction and urinary disorders. In particular, dyspepsia and psychogenic dysuria often develop in anxious patients.
Impotence, and sometimes the risk of possible sexual dysfunction, is difficult for the patient to tolerate. Frequent mood swings, irritability, obnoxiousness, excessive concern for their own health, even "concern about illness".
symptoms
In the absence of prompt treatment of acute prostatitis, there is a high risk of developing a prostate abscess. With the formation of a fovea, the patient's body temperature rises to 39-40 ° C and can become busy in nature. Periods of heat alternate with severe chills. The sharp pain in the perineum causes difficulty urinating and defecating.
An increase in prostate edema leads to acute urinary retention. Rarely, an abscess spontaneously ruptures into the urethra or rectum. When opened, the urethra is cloudy, cloudy, with an unpleasant pungent odor, when opened, there is pus and mucus in the rectum.
Chronic prostatitis is characterized by an undulating process with long periods of remission, in which inflammation in the prostate is latent or manifested by extremely poor symptoms. Patients who don't bother about anything often stop treatment and only come back when complications develop.
The spread of urinary tract infections causes pyelonephritis and cystitis. The most common complications of the chronic process are inflammation of the testicles and epididymis (epididymitis) and inflammation of the seminal vesicles (inflammation of the seminal vesicles). The result of these diseases is often infertility.
diagnose
The characteristic clinical picture simplifies the diagnosis of acute and chronic prostatitis. It is required to:
Prostatitis treatment
Treatment of acute prostatitis
Patients with an uncomplicated acute course are treated by a urologist on an outpatient basis. With severe intoxication, suspected pus, hospitalization is indicated. Antibacterial therapy is performed. Preparations are selected taking into account the susceptibility of the infectious agent. Widely used antibiotics are able to penetrate well into prostate tissue.
With the development of acute urinary retention in the setting of prostatitis, they use bladder catheterization and not urethral catheterization, since there is a risk of prostate abscess formation. With the development of an abscess, endoscopic or transurethral opening of the abscess is performed.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
Treatment of chronic prostatitis should be complex, including drug therapy, physiotherapy, immunomodulatory:
- antibiotic therapy. Patients are prescribed antibacterial drugs for a long time (within 4-8 weeks). The selection of the type and dosage of antibacterial drugs, as well as the determination of the duration of the course of treatment are carried out individually. The drug is selected based on the sensitivity of the microflora according to the results of urine cultures and prostate secretions.
- prostate massage.Gland massage has a complex effect on the affected organ. During massage, inflammatory secretions that accumulate in the prostate are forced out into the ducts, then enter the urethra and are excreted from the body. The procedure improves blood circulation in the prostate, which helps to minimize congestion and ensure better penetration of antibacterial drugs into the tissue of the affected organ.
- physical therapy.To improve blood circulation, laser exposure, ultrasonic waves and electromagnetic vibrations are used. If it is not possible to carry out physiotherapeutic procedures, the patient is prescribed a warm drug microclyster.
In the case of chronic, long-term inflammation, consultation with an immunologist is indicated to select immunotherapy tactics. Patients are counseled on lifestyle changes. Making certain changes in the lifestyle of patients with chronic prostatitis is both a curative and a preventive measure. The patient should normalize sleep and alertness, establish a diet, conduct moderate physical activity.
For the treatment of prostatitis, antibiotic therapy is the most effective. Botanical therapies, immunomodulators, and hormonal preparations may also be used as directed by your doctor.
In the absence of acute symptoms, prostatitis can be treated with physical therapy methods. In the case of abscesses and pus, surgical intervention is recommended.
Drug treatment
Treatment of prostatitis with antibiotic therapy should begin with bakposv, the purpose of which is to assess the body's sensitivity to this antibiotic. Violation of urination, a good result is the use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
The drug is administered in the form of tablets, in acute cases - in the form of a dropper or intramuscularly. For the treatment of chronic forms of prostatitis, rectal suppositories are effective: with their help, the drug reaches its target faster and has a minimal effect on other organs.
Blood thinners and anti-inflammatory drugs have also been shown to be good.
antibacterial therapy
Antibiotics are an effective remedy in the fight against bacterial prostatitis. In order to achieve the desired effect and not harm the body, the choice of drug, dosage and treatment regimen should be handled by a doctor. In order to correctly choose the most effective drugs, he will have to find out what kind of pathogen causes prostatitis, and at the same time test the patient's tolerance to antibiotics of a particular group.
For the effective treatment of chronic prostatitis, fluoroquinolone antibiotics have been shown to be good. Their action is aimed at preventing bacterial infections and strengthening the body's immunity. In addition, a bacteriostatic antibiotic is recommended for the prevention and treatment of concomitant diseases of the genitourinary system.
Treatment of mycoplasma and chlamydial prostatitis can be supplemented with macrolides and tetracyclines, which slow the spread of the infection.
The duration of antibiotic treatment is from 2 to 4 weeks. In the case of positive momentum, the course can be extended.
physical therapy
Physiotherapy methods in the treatment of prostatitis are aimed at activating blood circulation in the pelvic region, improving metabolism in the prostate gland, and clearing the ducts. If physiotherapy is combined with the use of antibiotics, then the effect of the latter will be enhanced.
The main methods include:
- therapeutic magnetic field;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- heat up;
- supersonic;
- Sludge treatment;
- high frequency irradiation;
- physical therapy.
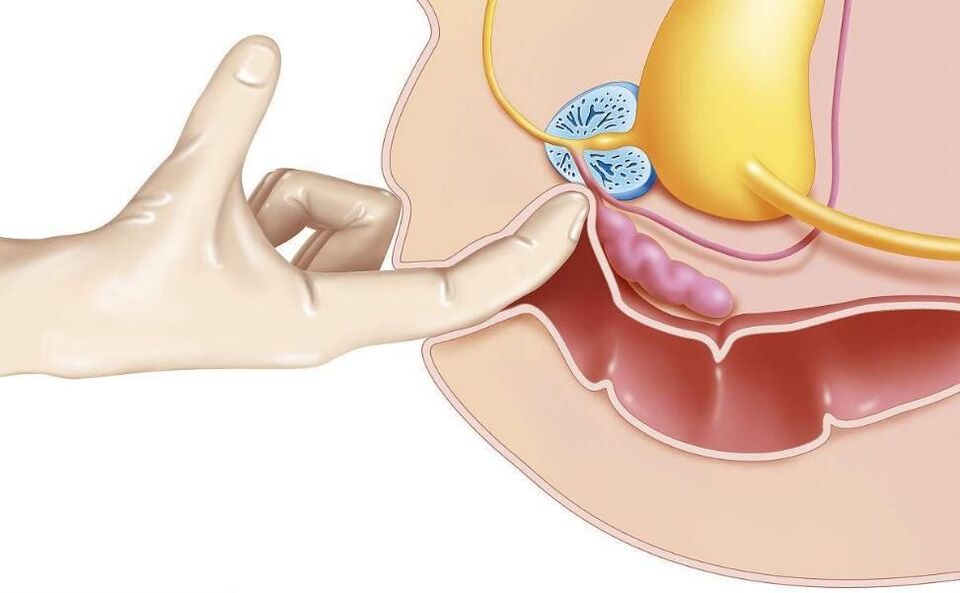
One of the oldest methods - rectal massage of the prostate gland, which, according to modern research, has no proven effectiveness.
Non-specific treatment
Nonspecific treatments for prostatitis include:
- hirudotherapy;
- fasting healing;
- Acupuncture;
- diet according to the method of Ostrovsky;
- Alkalize the body by the Neumyvakin method.
All non-traditional prostatitis treatments are recommended in collaboration with your doctor.
Surgery
Surgical methods are used in complex and urgent cases:
- to drain a purulent abscess, which is removed endoscopically through a puncture;
- violation of urination due to damage to the urinary tract;
- with a large volume of the affected area;
- with a significant number of stones in the body of the gland.
Stones and fibrous tissue are removed endoscopically. With large lesions or many stones, people resort to the method of prostatectomy.
Transurethral resection is also effective for bacterial prostatitis. As a result, the risk of disease recurrence can be reduced.
folk remedies
Treatment of prostatitis with folk remedies can hardly be effective on its own, but can be applied in combination with medical methods and physical therapy. These include: beekeeping products, decoctions of herbs and seeds, garlic wine, ginger, beaver, fresh vegetables, pumpkin seeds.
In acute cases of the disease process, you must consult a doctor, and in no case should you self-medicate! In case of rupture of a purulent abscess, it can be fatal.
Candles for prostatitis
Treating prostatitis with rectal suppositories is much more effective than pills, if only because the rectum is much closer to the prostate, meaning that the medicine will work faster.
The composition of drugs for the treatment of prostatitis can be completely different, they are prescribed to solve a specific problem.
- Antibacterial agents are particularly effective against chlamydial prostatitis.
- Analgesics are used to treat symptoms, they provide good pain relief.
- Immunostimulators improve blood circulation, reduce swelling and are used in complex therapy.
- Phytopreparations have a mild effect. They, like the candles on bee products, are used as a supplement to the main treatment.
- Preparations based on ichthyol promote blood flow in the area of the intestinal mucosa, which accelerates inflammation and slightly improves immunity.
- Enzyme-based products prevent the formation of scar tissue. Should be used as part of complex therapy with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs.
Support medicine
To treat symptoms of prostatitis in men, such as pain when urinating, you can add an antispasmodic drug that relaxes smooth muscle and thus quickly relieves pain.
Blood-thinning and anti-inflammatory dietary supplements based on bee products, pumpkin seed oil, palm fruit extract contribute to overall recovery.
Diet and lifestyle
To treat prostatitis, a proper, balanced diet and healthy lifestyle are very important. Food should not contain a lot of spices, fried, salty, pickled. In acute form, alcohol is strictly prohibited.
Food should contain enough fiber to prevent constipation. Protein content should be reduced. It is recommended to supplement the diet with herbs, ginger, pumpkin seeds.
Non-drug treatment
Non-drug therapies allow you to act directly on the prostate gland, increasing the concentration of the drug in its tissues, helping to eliminate blockages.
Microwave hyperthermia is performed using a rectal probe inserted into the patient's anus. On the device, you can set the temperature required for a particular type of exposure. In order to increase the concentration of the drug in the prostate, it is necessary to heat it to 38-40°C. To obtain an antibacterial effect - 40-45 ° C.
Today, non-drug treatments focus on laser therapy. The possibilities of this technique are very wide. Under the influence of the laser, the following processes occur in the prostate gland:
- activation of redox reactions;
- improves blood microcirculation;
- new capillaries are formed;
- pathogenic microflora is inhibited;
- the process of cell division is activated, which contributes to tissue regeneration.
During the study of the effects of laser therapy on patients with prostatitis, a side effect was observed but positive for therapeutic purposes. In those who complete the course, potency increases, erectile dysfunction is eliminated and vitality is restored. To achieve this result, it is necessary to use a beam of a certain wavelength. In general, low-intensity laser radiation is used to treat chronic prostatitis.
Patients can actively undergo a course of laser treatment, if not indicated by the attending physician.
Surgical treatment of chronic prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis is not life-threatening but can significantly reduce quality of life. The most serious complication of this disease is the formation of stones in the tissues of the gland. To free it from prostoliths, transurethral resection is used.
Surgery was performed under the control of TRUS.
If complications such as prostate sclerosis occur, transurethral electrocautery is performed. If in combination with this pathology, sclerosis of the bladder neck is observed, then a partial prostatectomy is performed.
With obstruction of the vas deferens and excretory ducts, endoscopic operations are indicated in order to eliminate violations of the tenacity of the secretory. For this purpose, an incision is made in the seminal vesicles and excretory ducts. With an abscess, it is possible to completely remove the gland.
Consequences of untreated prostatitis

Even if the symptoms of prostatitis do not appear for a long time, it is necessary to regularly check with a urologist. Prostatitis that is not completely cured may be accompanied by calcification, which must then be removed along with the gland. Experts are sure that there is no other way to remove or dissolve stones.
In addition, pathogenic microorganisms can migrate to nearby organs, causing inflammation. Running prostatitis can cause the development of adenomas and prostate cancer.
Forecasting and prevention
Acute prostatitis is a disease with a marked tendency to turn chronic. Even with timely adequate treatment, more than half of patients still have chronic prostatitis. Recovery is not always achieved, however, with the correct therapy and following the doctor's recommendations, it is possible to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and achieve stable remission. permanent in a chronic process.
Prevention is about eliminating risk factors. It is necessary to avoid hypothermia, alternating between sedentary work and physical activity, and eat a balanced and adequate diet. For constipation, laxatives should be used. One of the preventive measures is to normalize sex life, as both excessive sexual activity and sexual abstinence are risk factors for prostatitis. If symptoms of urinary or sexually transmitted diseases appear, you should consult a doctor in time.